Intellectual Property Rights Policy
At Coupang, we take Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) seriously and appreciate our sellers who work hard to comply with the law and Coupang policies. Repeated instances of IPR violations can result in account suspension and other penalties for sellers, so please take a moment to review this important information on IPR.
This policy provides a general overview of intellectual property rights (IPR). Sellers on Coupang should comply with all applicable laws/regulations and Coupang policies and not infringe on the intellectual property rights of other owners. Please refer to the policies below for selling products.
For further details on the appeal documents, please click the links below:
📌[Guidelines on appeal documents for verification of distribution routes]
📌[Guidelines on appeal documents for Intellectual property right infringement]
What are intellectual property rights?
Intellectual property rights are the rights associated with the creation of the right owner for a specific period of time, and are organized into four main categories. We’ve enclosed definitions of each type of IPR as well as the different types of infringements.
- Trademark: A word, symbol, or logo used on the right owner’s product to distinguish it from the products of others.
- Copyright: Works directly created by the author, such as images, videos, drawings, etc.
- Design: Exclusive rights to a form, shape, and color of the product (including parts of the product and the typeface).
- Patent: Exclusive rights to use or sell the creation of the IPR owner who devised the technical ideas.
Examples of Intellectual Property Infringement:
📌1. Trademark Infringement
- 1) Definition
The use of a trademark identical or similar to a registered trademark by a person other than the trademark owner registered with the Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPRIS) on products identical or similar to the designated ones without due authority.
- 2) Examples
(1) Selling a product including a specific brand logo even when the product is not manufactured by that brand
Example) If Seller A registered the trademark ‘MAHTO’ on KIPRIS, and Seller B sells a product by attaching the same trademark without the right owner’s permission, it constitutes trademark infringement.
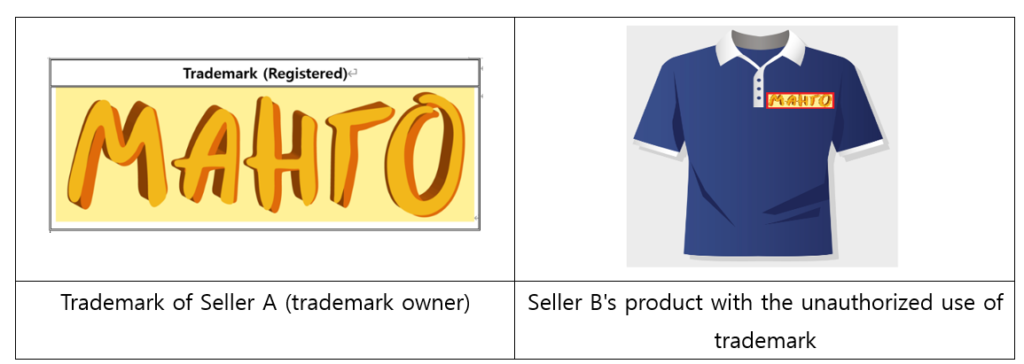
(2) Using another brand’s trademark in the name or description of the product not manufactured by that particular brand (exceptionally allowed for some compatible products).
- 3) Non-infringement cases
(1) Where it is possible to prove that the product is legitimate one from the trademark owner.
(2) Where permission to use is granted by a legitimate trademark owner.
- 4) How to prevent trademark infringement
(1) Do not use trademarks registered by others on detail pages or SDP without permission.
(2) Do not sell counterfeit products.
(3) Only list relevant trademarks in product names, detailed descriptions, etc.
📌2. Copyright infringement
- 1) Definition
Unauthorized use of copyrighted works, such as product images and videos, without permission from the original author
- 2) Infringement cases
A) Selling a product with the work of the original author attached on it without permission.
Example) Seller B sells a product with Seller A’s copyrighted work attached.

B) Where the original author posts a picture of the product on his/her website and uses this picture on his/her detailed page without due permission.
Example) If Seller A took a picture of his/her product and uploaded an image, and Seller B, who saw it, captured the product image (copyrighted work) without permission, and used it on his/her detailed page, it is a copyright infringement because s/he used the picture without permission from the original copyright owner.

C) Selling unauthorized copies of media such as books, movies, music, artwork, paintings, etc.
Example) If a seller downloads a movie distributed via Blu-ray to a USB and sells it, it is a copyright infringement.
- 3) Non-infringement cases
A) Where the legitimate copyright owner’s permission is obtained.
If the permission to use copyright is obtained from the original copyright owner or a transfer contract is signed, it is not a copyright infringement. In this case, if you submit evidentiary documents and indicate in the appeal form that you have obtained permission to use it, Coupang will review it and lift the sale suspension.
- 4) How to prevent copyright infringement
A) If you want to upload an image of the product to the detailed page, upload only the images you created yourself.
B) If you intend to use the copyrighted work of someone else, you must obtain permission from the original copyright owner and have the relevant documents as proof.
📌3. Design infringement
- 1) Definition
Using a design that is identical to a design right registered with the Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPRIS) without permission.
- 2) Infringement cases
A) Where a seller produces and sells a product that imitates the design registered by the right owner with the Korean Intellectual Property Office without permission.
Example) Seller A registered a design for a bag with a rectangular shape and lattice stitching, and as the design became popular, Seller B produced and sold a bag with a similar design.
This is an infringement of design rights because the design right was used without permission of the design right owner.
- 3) Non-infringement cases
A) Where the legitimate design right owner’s permission is obtained
It is not an infringement of design right if the design right owner’s legitimate permission is obtained. In this case, if you submit the relevant documents along with the appeal form, Coupang will review them and lift the sale suspension.
- 4) How to prevent design infringement
Do not sell products imitating the design of other products or sell products protected by design rights.
📌4. Patent infringement
- 1) Definition
Patent infringement refers to the act of copying or using a patent registered with the Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPRIS) without permission.
- 2) Infringement cases
A) Where a person who does not hold the right to a patented technology registered with the Korean Intellectual Property Office sells the product using the technology without permission
Selling a product that uses the technology registered with the Korean Intellectual Property Office without permission constitutes an infringement of patent rights.
Example) If Seller A invented and registered a patented technology that emits music with LED light in the fan, and Seller B borrowed this technology without permission to sell the product, it is a patent infringement.
- 3) Non-infringement cases
B) If the permission to use patented technology is obtained
: If the permission to use the patented technology is obtained from the original patent right owner or a transfer contract is signed, it is not a patent infringement.
- 4) How to prevent patent infringement
Do not sell imitations of patented products without permission or license from the patent owner.
FAQ
For frequently asked questions, please click the link below.
For a downloadable guide, click here. As a Coupang seller, you may find yourself reporting an IPR violation or addressing or receiving an IPR infringement notice. If you would like to report a violation, please head to https://www.coupang.com/np/safety/compliance. If you have any questions, please don’t hesitate to reach out to your respective Account Manager or the friendly team at helpseller_global@coupang.com.
For more tips on becoming a better seller, read up on our tips at Seller University.



